-
 Sold out
Sold outPremium Gauze Hand Wraps
Regular price $27.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
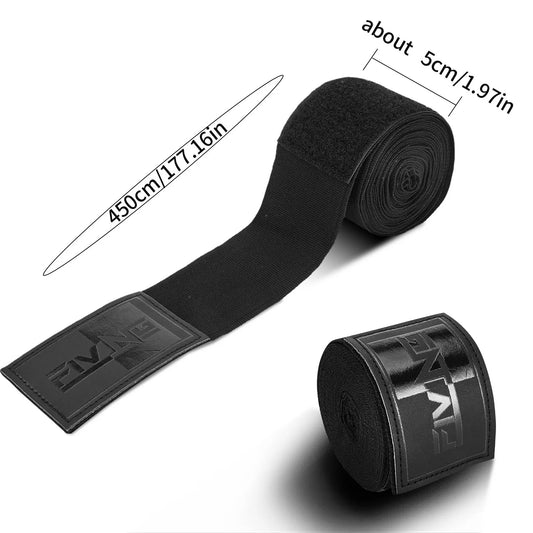
Breathable Stretch Hand Wraps, 300 & 500cm
Regular price From $18.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Stretch Hand Wraps, 150 cm/59"
Regular price $15.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
75% Cotton Hand Wraps
Regular price From $11.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per$13.89 USDSale price From $11.89 USDSale -
Quick Hand Wraps with Long Wrist Strap
Regular price $16.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per$20.89 USDSale price $16.89 USDSale -
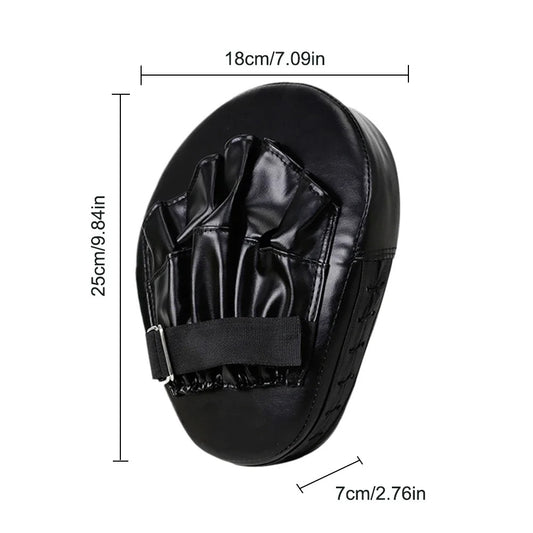
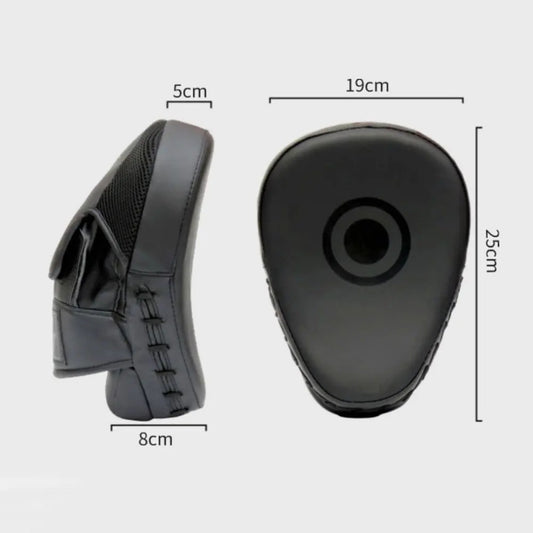
Curved Punching Mitts for Speed Training, 2 packs
Regular price $19.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Durable Punching Mitts, Unisex
Regular price From $26.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
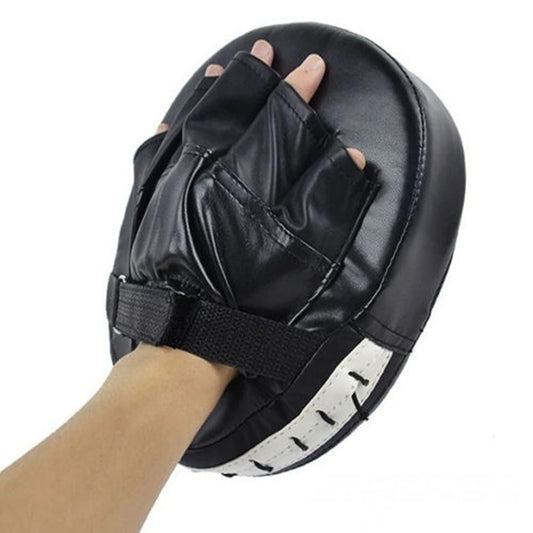
 Sold out
Sold outThick Kick Glove Pads
Regular price From $11.59 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Back Support Brace / Posture Corrector, Unisex
Regular price From $28.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Silicone Compression Ankle Brace, Pain Relief & Stability Support
Regular price $12.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Copper Compression Gloves, Pain Relief & Enhanced Mobility
Regular price From $11.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Copper Compression Leg Sleeve, Pain Relief & Support
Regular price $17.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
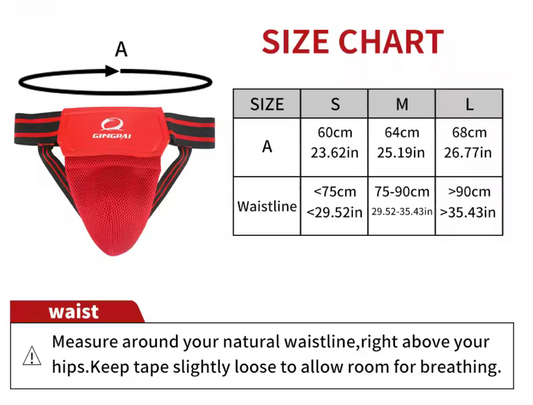
Groin Guard, Protection for Sports
Regular price From $16.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per
Purpose of Hand Wraps
Support and Alignment
They stabilize the bones and joints in the hand and wrist, keeping them properly aligned during the impact of punches. This helps prevent sprains, fractures, and dislocations.
Padding and Protection
Wraps add a layer of padding over the knuckles, protecting the skin from abrasions and cushioning the impact on the small bones.
Compression
They compress the soft tissues in the hand, lending strength and reducing movement of the bones upon impact.
Hygiene
Wraps absorb sweat, which helps to keep the inside of gloves cleaner and reduces odor.
Enhanced Punching Force
The added stability and compression from wraps may contribute to a more solid and potentially more forceful punch.
Types of Hand Wraps
Traditional/Cloth
Non-elastic or slightly elastic pieces of woven cotton or a cotton blend
- Customizable support depending on wrapping technique, generally durable and cost-effective.
- Can take time and practice to learn proper wrapping technique, can be uncomfortable if wrapped incorrectly.
Tape and Gauze
Often used by professional fighters in competitions. This method involves layering soft, absorbent gauze over the knuckles and hand, secured with athletic tape.
- They're known to be most protection, lightweight, allows for precise customization.
- Some tapes are not reusable.
Elastic/Stretch
Also referred to as “Mexican-style” hand wraps, made from a blend of materials, elastic fibers like polyester.
- This gives them a noticeable stretch and elasticity compared to traditional, non-elastic cloth wraps.
- Due to the elastic materials, can be easier to wrap too tightly.
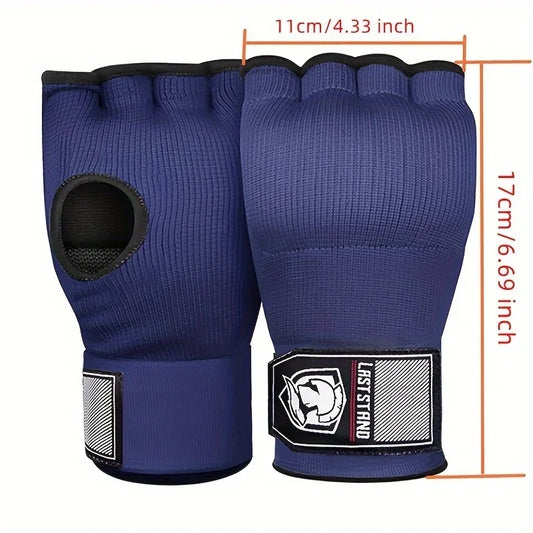
Quick Wraps (Inner Gloves/Gel Wraps)
These are pre-formed gloves, often with gel or foam padding over the knuckles. They slip on like gloves and usually have a wrist strap for added support.
- Quick and easy to apply
- The padding provides cushioning for the knuckles.
- Some offer minimal wrist support compared to traditional wraps.